Female Pattern Baldness: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Female pattern baldness can affect over 50% of women over the age of 50, according to the american hair loss association.
In this article, we discuss the causes of female pattern hair loss, treatment and regrowth options.
Short Summary
-
Female Pattern Baldness is a common hair loss disorder caused by genetic, hormonal and other factors.
-
Treatments such as minoxidil, oral medications, natural remedies and hair transplantation are available to manage the condition.
-
Prevention methods include hormone balancing on scalp, proper nutrition and stress management for healthy hair growth.
Understanding Female Pattern Baldness
There are different types of hair loss, and it's important to understand these types to create a treatment plan.
A subtle change in your hair parting, a handful of lost hair strands on your pillow, or a clogged shower drain may all seem ordinary until you realize that your part is becoming more visible.
This condition, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common female hair loss disorder that affects women and individuals assigned female at birth, impacting the hair shaft and causing hair shedding.
While it is often overshadowed by male pattern hair loss, it is essential to address and understand the unique challenges of female pattern hair loss.

I LOVE MY HAIR NOW
FullyVital hair serum and hair vitamins made tremendous improvements in my hair. I truly love my hair now.
Dorit S.,
Definition and Prevalence
Female pattern baldness affects a significant number of women, with the frequency increasing with age.
According to statistics, female pattern hair loss affects about 50% of women aged 50 and older.
As age progresses, female pattern baldness worsens, making it a growing concern for many.
But remember, it’s not exclusive to the elderly, women in their 30s and 40s can frequently experience hair loss.
Difference from Male Pattern Baldness
How does female pattern baldness differ from its male counterpart?
The answer lies in the pattern of hair loss. Male pattern baldness often follows the path of a receding hairline, leading to total hair loss in certain areas.
In contrast, hair loss in women happens in a more subtle way.
The thinning is primarily on the crown and top of the scalp.
Women do not typically lose all their hair like men do, but there is significant thinning that the scalp shines through.
It's important to note that female pattern hair loss is different from telogen effluvium.
Just like men, a thinning and shining scalp can be a cause of major embarrassment and anxiety for women.
Causes of Female Pattern Baldness
Female pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia is attributed to multiple factors - genetic, hormonal, and others such as age and endocrine conditions.
Understanding the underlying causes of female pattern baldness is the first step in finding the right treatment.
Though women exhibit diffuse hair loss as compared to men, the causes behind female and male baldness are the same.
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal fluctuations play a crucial role in the progression of female pattern baldness.
In women, the hormonal changes occur due to menopause or conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
Every woman has low levels of male hormones in her body.
Testosterone converts to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is the main hormone associated with hair loss in women and men.
Experts believe that DHT causes the hair follicles to shrink over time, leading to thinning hair in the areas of affected hair follicles.
DHT causes progressive thinning of the hair follicles, so hair becomes thinner and wispier until is stops growing.
At this stage, the hair follicle can become dormant.
Leading up to menopause, women's progesterone and estrogen start to decline.
This leads to a relative imbalance with testosterone, which converts to DHT and starts the hair thinning.
This hormonal imbalance is also observed in women with PCOS.
It's important to address female pattern hair loss before the hair follicle becomes dormant.
Genetic Factors
Genetics are quite important for female pattern baldness.
Just as you inherit your mother’s eyes or your father’s smile, the genes responsible for this condition can be passed down from either parent.
When you have genes responsible for hair loss, your hair follicles are more susceptible to the effects of normal male hormones or androgens in your body.
This means that even without an increase in levels of circulating DHT in your body, you can start losing hair.
Unfortunately, there is no known cure for female pattern baldness. However, there are treatments available.
Other Contributing Factors
Other factors that may contribute to female pattern baldness are stress, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medications.
It’s important to address these areas as well for best results.
Female pattern baldness is different from alopecia areata, which is caused by the immune system attacking the hair follicles.
Diagnosis of Female Pattern Baldness
Diagnosing female pattern baldness requires a comprehensive review of medical history and a thorough physical examination.
It is important to understand the underlying causes of female pattern baldness in order to properly diagnose and treat it.
Physical Examination
A dermatologist assesses the scalp, paying special attention to the occipital area, which often displays a widening of the central part with a diffuse decrease in hair density over the frontal scalp.
This can be indicative of a variety of conditions, including androgenic alopecia.
Blood tests may be required to check levels of hormones and vitamins in the individual.
Medical History
A dermatologist may also look for signs of hormonal imbalances or other medical conditions that could contribute to pattern hair loss in women.
These conditions can range from thyroid issues to autoimmune diseases, and even certain medications.
The doctor will treat each condition to fight hair thinning.
Differentiating from Other Hair Loss Conditions
It's important to differentiate female pattern baldness from other hair loss conditions for the best treatment plan.
It's not uncommon to be experience multiple types of hair loss at the same time. Each type of hair loss must be addressed for best results.
The dermatologist uses a combination of medical history and physical examination to make an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Female Pattern Baldness
There are various options available to treat female pattern baldness.
These include topical and systemic drugs, natural solutions, or in-clinic treatments, each with its own mechanism of action, benefits, and potential side effects.
Topical treatments are applied directly to the scalp and can include the following.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is the only drug approved by the FDA for the treatment of female pattern baldness.
It improves circulation to the scalp and can stimulate hair growth by elongating the anagen phase of the hair cycle, which means your hair spend more time in the growth phase.
Women are advised are used to apply 2% minoxidil or rogaine foam twice a day, or 5% minoxidil once a day.
This drug works by increasing the blood flow to the scalp, which in turn increases the amount of the nutrients and support to the hair strands.
Some practitioners have started prescribing low dose oral minoxidil for female hair loss, but this can also come with side effects.
Oral Medications: Spironolactone
Spironolactone, often used as a medication for treating high blood pressure and heart failure, has also gained recognition for its role in treating female pattern hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia.
This off-label use capitalizes on the drug's antiandrogen properties.
Spironolactone works by blocking the effects of DHT, thus potentially slowing or halting hair thinning and loss.
Clinical studies have shown spironolactone to be a potential treatment option for women with hair loss, particularly those unresponsive to topical minoxidil.
However, it's not without side effects.
These may include increased urination, irregular menstruation, fatigue, and potential harm to a developing male fetus; therefore, it's not recommended for women planning to become pregnant.
Oral Medications: Finasteride
Finasteride is a medication initially approved for treating prostate enlargement in men and later, male pattern baldness.
It works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that can contribute to hair follicle shrinkage and hair loss.
While finasteride has been successful in treating male hair loss, its use in women is more complex and not as well-studied.
Some clinical trials have shown that finasteride can help slow hair loss and stimulate hair growth in women, especially in postmenopausal women, who have lower levels of endogenous hormones.
However, finasteride is generally not the first-line treatment for female pattern hair loss due to its potential side effects and risk to fetal development.
Women of childbearing age should avoid finasteride, as it can cause birth defects in male fetuses.
Side effects can include changes in sexual function and mood changes, among others.
Furthermore, as with other hair loss treatments, it may take several months to notice any improvement.
Before starting finasteride, women should have a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider to understand its potential risks and benefits.
Hair Transplantation
Hair transplant surgery is a procedure that involves removing hair follicles from one part of the scalp, known as the donor area (usually the back or sides where hair is more resistant to balding), and transplanting them to the thinning or balding areas.
This surgical option is often considered when non-surgical treatments have not provided satisfactory results.
While hair transplants are more commonly associated with androgenetic alopecia in males, they can also be a viable option for some women suffering from female pattern baldness.
However, the success and suitability of hair transplants for women depend on various factors.
Women with diffuse thinning, where thinning occurs all over the scalp, might not have a sufficient donor area, making the procedure challenging.
However, for women with hair loss mainly at the top of the scalp and a healthy density of hair at the back and sides, a hair transplant may be effective to restore hair growth.
It's important to discuss this option in detail with a renowned hair transplant surgeon.
Alternative Treatments
Alternative treatments for female pattern baldness can include hair growth supplements, hair serums, laser therapy, platelet-rich plasma therapy and exosomes.
They show promise in their ability to treat hair loss, stimulate regrowth, but their effectiveness is still being investigated.
For example, natural ingredients such as topical caffeine have shown to reduce the hair shrinking effects of DHT.
Saw palmetto and other natural DHT blockers can be taken orally to reduce DHT levels in the body.
These treatments are not yet widely accepted by the medical community, but they are gaining traction as more people use them.
Prevention and Hair Care Tips
Certain measures may help maintain hair health. Your hair needs care, nutrition, and stress management for it to grow normally, especially as you age.
Taking care of your hair is essential for keeping it healthy and strong.
Gentle Hairstyling
Gentle hair styling is important to prevent unnecessary stress.
Avoiding tight hairstyles, minimizing brushing, and limiting the use of long-lasting hold styling products can go a long way in preventing hair breakage and damage.
These simple steps can help keep your hair healthy and strong, while still allowing you to express yourself.
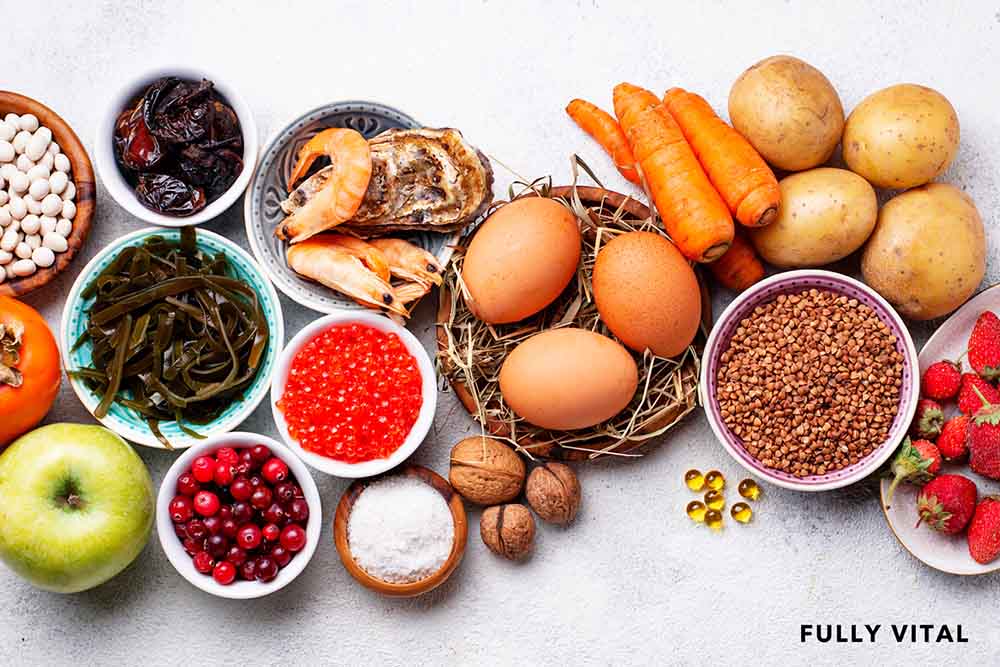
Proper Nutrition
Proper nutrition is like the fuel your hair needs to thrive.
A diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals can support healthy regrowth.
Processed foods, sugary foods, and foods high in saturated fat should be avoided. Enhance hair growth vitamins can help provide the nutrition your hair follicles need.
Stress Management
We live in stressful times. Stress has been linked to a shorter hair growth cycle.
It's important to balance stress for healthy hair.
Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and exercise can help reduce hair loss caused by stress.
These techniques can help you manage your stress levels and keep your hair healthy.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies
Navigating the journey of female pattern baldness can take a toll on mental well-being.
But remember, you’re not alone. Emotional support and coping strategies can guide you towards mental peace.
Solutions To Hide Female Pattern Hair Loss In Women
Practical solutions such as wigs, hairpieces, and hair styling techniques can help individuals feel more confident and comfortable with their appearance.
These solutions can be tailored to each individual’s needs and preferences, allowing them to express themselves.
But these are temporary solutions. It's best to address female pattern hair loss at the root to avoid progression of hair thinning. It's also important to rule out traction alopecia, which is another type of hair loss.
Summary
Millions of women suffer from androgenetic alopecia or female pattern baldness, but it’s not without hope.
It's important to pay attention to increased hair shedding and take action early.
From understanding the causes to exploring various hair loss treatment options and adopting hair care tips, you can stop and in many cases regrow hair.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does hair grow back with female pattern baldness?
Unfortunately, female pattern baldness is permanent if left untreated.
However, treatment can help to promote hair regrowth and maintain existing hair. It's also known as androgenetic alopecia or androgenic alopecia.
Can female pattern hair loss be fixed?
Female pattern hair loss can be treated, but there is no cure.
Common treatments may include over-the-counter medications applied to the scalp, prescription oral medications, natural hair growth supplements and hair serums.
Results vary depending on the person, but treatment may slow down or stop hair loss and potentially stimulate hair regrowth.
Can you do anything about female pattern baldness?
Minoxidil, an FDA-approved medicine for female pattern baldness, may help regrow hair in 1 in 4 or 5 women.
It is applied to the scalp and is available in 2% solution or 5% foam.
The 2% solution is applied twice daily, while the 5% foam is applied once daily.
Minoxidil is generally well tolerated, but some women may experience scalp irritation or itching. It is important to follow the instructions for correct usage.
What are the beginning stages of female pattern baldness?
Female pattern baldness typically begins with thinning hair across the top and crown of the scalp, often accompanied by a widening of the center part.
This type of hair loss is most common in women over the age of 50, but it can occur at any age.
It is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, and is not reversible but can be managed with the right approach.
Treatment options include medications and natural ingredients.
What is female pattern baldness?
Female pattern baldness is a common hair loss disorder that affects women, characterized by thinning and hair loss on the scalp.
It is estimated that up to 50% of women over the age of 50 experience some degree of hair loss.
The cause of female pattern baldness is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to female pattern baldness.
Are there any other types of hair loss types?
The other types of hair loss include traction alopecia and scarring alopecia.