Hair-pulling: Importance Of Hair-Pulling Awareness
As a woman seeking to stimulate hair growth, you might have come across the term "hair-pulling" in your search for effective solutions.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore what hair-pulling is, why it's essential to be aware of it, how it works, its causes, potential downsides, and alternative approaches.
Our goal is to provide valuable information to all women of different hair types looking to stimulate hair growth.

I LOVE MY HAIR NOW
FullyVital hair serum and hair vitamins made tremendous improvements in my hair. I truly love my hair now.
Dorit S.,
What Is Hair-pulling?
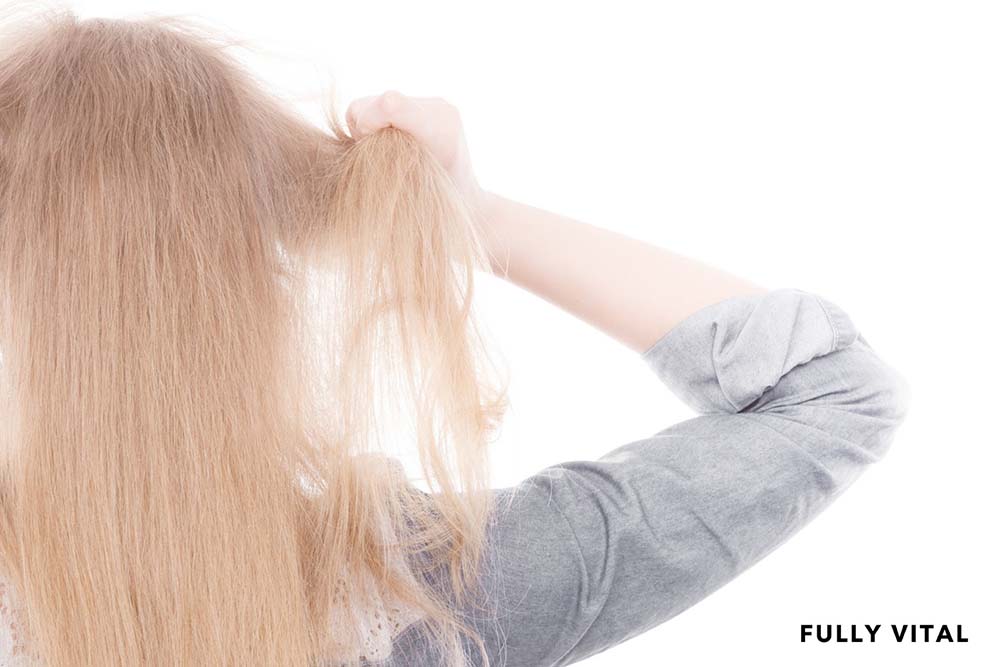
Hair-pulling, medically known as trichotillomania, is a psychological disorder that involves the irresistible urge to pull out one's hair.
This condition can affect people of all ages, including women with various hair types.
The Hair-pulling behavior can involve the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or any other body area with hair.
It is essential to understand that Hair-pulling is not a simple habit; it's a complex disorder that requires attention and understanding.
People with trichotillomania often experience intense urges or tension before pulling their hair.
The act of pulling then provides a sense of relief or gratification, reinforcing the behavior.
Over time, it can become a repetitive and challenging pattern to break.

Why Is Hair-pulling Awareness Important?
Raising awareness about Hair-pulling is crucial for several reasons.
Firstly, many individuals suffering from trichotillomania may not even be aware of the condition or that it can be managed.
By creating awareness, we can help people recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate support and treatment.1
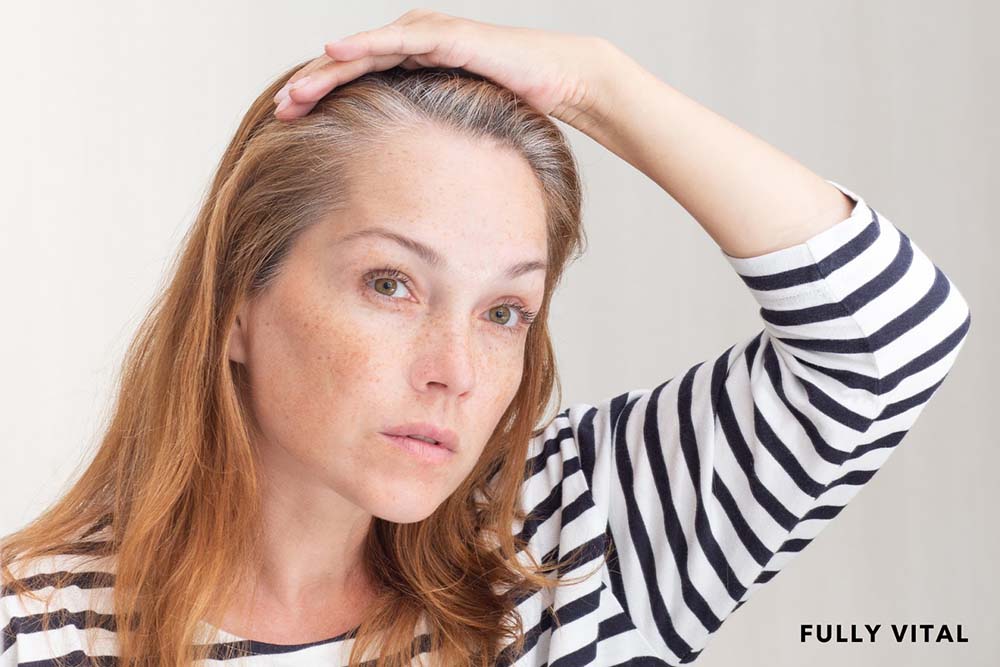
Hair-pulling can be a distressing experience for those affected, leading to emotional and psychological challenges.
Breaking the stigma around Hair-pulling can encourage affected women to open up about their struggles, leading to a supportive community where they can share experiences and advice.
Moreover, increased awareness promotes research into better solutions for managing Hair-pulling effectively.
As we learn more about the causes and triggers of trichotillomania, we can develop more targeted and effective interventions to support women in their hair growth journey.
How Does Hair-pulling Work?
The exact cause of trichotillomania is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Some people may have a genetic predisposition to trichotillomania, meaning it can run in families.
However, not everyone with a family history of Hair-pulling will develop the condition.2
For many individuals, Hair-pulling is often associated with stress, anxiety, or other emotional triggers.
When they encounter stressful situations or experience heightened emotions, they may find relief by engaging in Hair-pulling.
This act of pulling provides a temporary escape from the emotional distress they are facing.
The continuous repetition of this behavior can lead to a cycle of Hair-pulling that becomes difficult to control.
The brain forms associations between stress relief and Hair-pulling, making the behavior more automatic over time.
What Are The Causes Of Hair-pulling?
While the precise causes of Hair-pulling may vary from person to person, some common factors can contribute to the development of trichotillomania:
Genetics
There may be a genetic predisposition to trichotillomania, meaning it can run in families.
However, genetics alone do not determine whether someone will develop the condition.
Stress And Anxiety
High levels of stress, anxiety, or other emotional triggers can exacerbate Hair-pulling behavior.
Stressful life events, such as major transitions or traumatic experiences, may also contribute to the onset of Hair-pulling.3
Trauma
Some individuals with trichotillomania have experienced traumatic events, which may be linked to the onset of the condition.
Hair-pulling may serve as a coping mechanism for dealing with the emotional aftermath of trauma.
Other Mental Health Conditions
Trichotillomania is often associated with other mental health disorders, such as depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
It is believed that there may be shared neurobiological mechanisms between these conditions.
It is essential to recognize that Hair-pulling is not a result of weakness or lack of willpower.
It is a complex psychological condition that requires understanding and support from both the affected individuals and those around them.
What Are The Harmful Effects Of Hair-pulling?
There are several downsides to Hair-pulling, both physically and emotionally:
Hair Loss
Frequent Hair-pulling can lead to noticeable hair loss and thinning, which can significantly affect an individual's self-esteem and body image.
The loss of hair can be particularly distressing, especially when it becomes evident to others.
Skin Irritation
Constant pulling can cause irritation and inflammation of the affected skin areas.
The repeated pulling action can lead to redness, soreness, and even small wounds on the scalp or other hair-bearing areas.
Social Impact
Hair-pulling may lead to social discomfort and withdrawal due to embarrassment about the visible consequences of the behavior.
Individuals with trichotillomania may feel self-conscious and avoid social situations to prevent others from noticing their hair loss.
Negative Emotional Impact
Dealing with trichotillomania can result in frustration, guilt, and diminished self-confidence.
Affected individuals may feel ashamed of their Hair-pulling behavior, leading to further isolation and emotional distress.
Time Consumption
Engaging in Hair-pulling can be time-consuming, as individuals may spend significant periods pulling their hair and managing the aftermath.
This time investment can interfere with daily activities, relationships, and responsibilities.
Cycle Of Guilt
Many individuals with trichotillomania experience guilt and shame after engaging in Hair-pulling.
The guilt can fuel a vicious cycle, where the negative emotions trigger further Hair-pulling as a way to cope with the guilt itself.
What are methods for preventing hair-pulling behavior?
If you're seeking alternatives to hair-pulling, consider the following approaches:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is considered one of the most effective treatments for trichotillomania.
Through CBT, you can work with a trained therapist to identify triggers and learn coping strategies to manage Hair-pulling urges effectively.
The therapy may also address any underlying emotional issues contributing to the behavior.
Acceptance And Commitment Therapy (ACT)
An act is another therapeutic approach that can be beneficial for individuals with trichotillomania.
It focuses on accepting difficult thoughts and emotions while committing to positive behaviors that align with one's values.
Mindfulness Techniques
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing, can aid in reducing stress and anxiety, potentially decreasing Hair-pulling tendencies.
Mindfulness techniques promote self-awareness and help individuals develop healthier responses to emotional triggers.
Support Groups
Joining a support group or seeking counseling can provide a safe space to share experiences and receive encouragement from others facing similar challenges.
The sense of belonging to a supportive community can be empowering and contribute to the healing process.
Stimulating Fidget Toys
Using fidget toys or stress balls can provide an outlet for restless hands and divert attention away from Hair-pulling.
Having a positive and tactile object to engage with can help break the automatic response of Hair-pulling.
Journaling
Keeping a journal to track Hair-pulling urges and emotions can be beneficial.
By identifying patterns and triggers, individuals can develop personalized strategies to prevent or manage Hair-pulling episodes.
Habit Reversal Training (HRT)
HRT is a specific behavior modification technique that focuses on replacing Hair-pulling with less harmful behavior.
This approach involves creating awareness of Hair-pulling triggers and consciously redirecting the urge into a different action.
Professional Haircare
Working with a hair care specialist who understands trichotillomania can be helpful.
They can recommend hairstyles and treatments that may conceal hair loss, making it less noticeable and lessening any self-conscious feelings.
Is Hair-pulling Related To Stress Or Anxiety?
Hair-pulling can indeed be related to stress or anxiety. For many individuals with trichotillomania, the act of pulling their hair provides temporary relief from stressful or anxious feelings.
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate Hair-pulling tendencies, leading to a vicious cycle where the behavior becomes a coping mechanism for emotional distress.
How Stress And Anxiety Influence Hair-pulling:
-
Stressful events or situations may trigger Hair-pulling episodes as a way to alleviate tension.
-
Anxiety can lead to restlessness, making individuals more prone to engaging in Hair-pulling behaviors.
-
High levels of stress can weaken self-control, making it harder to resist the urge to pull hair.
Coping Strategies to Manage Stress and Anxiety:
-
Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
-
Engage in regular physical exercise, which can release endorphins and improve mood.
-
Seek support from friends, family, or mental health professionals to address underlying stressors.
Can Certain Life Events Trigger Hair-pulling Episodes?
Yes, certain life events can trigger Hair-pulling episodes, especially for individuals susceptible to trichotillomania.
Major life transitions, traumatic experiences, or significant emotional upheavals may lead to increased Hair-pulling behaviors.
Common Triggers for Hair-pulling:
-
Loss or Grief: The loss of a loved one or dealing with grief can trigger Hair-pulling as a way to cope with overwhelming emotions.
-
Academic or Work Stress: High-pressure environments, such as exams or demanding work situations, can contribute to Hair-pulling episodes.
-
Relationship Struggles: Difficulties in personal relationships can lead to increased stress and emotional triggers for Hair-pulling.
Coping Strategies for Handling Triggers:
-
Recognize and identify personal triggers to better understand the root causes of Hair-pulling episodes.
-
Develop healthy coping mechanisms, such as journaling or talking to a therapist, to address emotional responses to triggering events.
-
Create a supportive environment with open communication to discuss and manage triggers effectively.
What Are Some Effective Coping Strategies For Managing Hair-pulling Urges?
Managing hair-pulling urges requires a combination of self-awareness and practical coping strategies.
By implementing the following techniques, individuals can gain better control over their hair-pulling behaviors.
Coping Strategies for Hair-pulling Urges:
-
Mindfulness Exercises: Engage in mindfulness techniques to increase awareness of hair-pulling urges and prevent acting on them impulsively.
-
Stimulus Control: Modify the environment to reduce access to hair-pulling triggers, such as removing tweezers or keeping hands busy with fidget toys.
-
Habit Reversal Training (HRT): Implement HRT techniques to replace Hair-pulling with less harmful behavior, like clenching a fist or squeezing a stress ball.
Distraction Techniques:
-
Physical Distractions: Engage in physical activities like exercise, drawing, or crafting to divert attention away from hair-pulling urges.
-
Mental Distractions: Keep the mind occupied with puzzles, games, or reading to reduce the focus on hair-pulling thoughts.
Self-Reflection and Support:
-
Identify Triggers: Reflect on the circumstances or emotions that precede hair-pulling urges to better anticipate and manage them in the future.
-
Support System: Seek support from friends, family, or support groups to share experiences and receive encouragement in managing hair-pulling urges.
Can Hair-pulling Become A Compulsive Behavior?
Yes, hair-pulling can become a compulsive behavior for individuals with trichotillomania.
Compulsive behaviors are actions that are difficult to control, often leading to repetitive and ritualistic patterns.
Signs of Compulsive Hair-pulling:
-
Frequent and uncontrollable urges to pull hair, even when the individual tries to resist.
-
Feeling a sense of relief or gratification after pulling hair, reinforcing the behavior.
-
Difficulty stopping the Hair-pulling behavior despite negative consequences.
Addressing Compulsive Hair-pulling:
-
Seek professional help from a mental health specialist experienced in treating trichotillomania.
-
Consider cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) to address the compulsive nature of Hair-pulling.
-
Combine therapy with self-help strategies to regain control over the Hair-pulling urges.
Are There Any Natural Remedies Or Supplements That May Help Reduce Hair-pulling Tendencies?
While there is no specific natural remedy or supplement that can cure Hair-pulling, some alternative approaches may complement traditional treatment methods.
Potential Natural Approaches:
-
Essential Oils: Some individuals find using essential oils like lavender or chamomile in aromatherapy helpful for relaxation and stress reduction.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Consult with a healthcare professional before considering any supplements, as certain vitamins and minerals may support overall well-being.
Complementary Therapies:
-
Yoga and Meditation: Practicing yoga and meditation can promote mindfulness and stress reduction, potentially reducing Hair-pulling tendencies.
-
Acupuncture: Acupuncture may help some individuals manage stress and anxiety, which could indirectly affect Hair-pulling behaviors.
Unlock The Secret To Youthful Locks With Fully Vital Hair Growth Products!Experience the transformation of your hair with Fully Vital's science-backed hair growth products. Say goodbye to the signs of aging and embrace a healthy relationship with your locks. Our powerful formulations are designed to slow down and even reverse the aging of your hair, giving you the confidence to shine from within. Key Features:
Benefits:
Discover the power of Fully Vital hair growth products and embrace the natural beauty of your hair. Let your locks shine, and embark on a journey towards a more vibrant and youthful you! |
Final Thoughts On Hair-pulling
Understanding Hair-pulling and its impact is essential for women of all hair types seeking to stimulate hair growth.
Trichotillomania is a complex psychological condition, often related to stress, anxiety, and other emotional triggers.
By raising awareness and providing valuable information, we can support those affected by Hair-pulling and promote a compassionate community.
Remember, hair-pulling can be managed with the right strategies and support.
If you or someone you know is struggling with hair-pulling tendencies seek professional help to develop personalized coping techniques.
Combining therapy, mindfulness, and self-reflection can help regain control over hair-pulling urges and promote healthy hair growth.
At Fully Vital, we are committed to helping you maintain a healthy relationship with your locks.
Our variety of hair growth products is designed to stop the aging of your hair and nurture its vitality. Embrace your hair's natural beauty and take the first step towards a confident, flourishing you.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hair-pulling
Is Hair-pulling treatable?
Yes, Hair-pulling is treatable, and various therapeutic interventions have shown positive results in managing the condition.
Seeking professional help and support is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan.
Is Hair-pulling More Common in Women than Men?
Yes, trichotillomania is more prevalent among women.
However, men can also experience the condition.
Can Hair-pulling be a symptom of another medical condition?
In some cases, Hair-pulling can be associated with certain medical conditions, but it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Is Hair-pulling a form of self-harm?
Hair-pulling is not considered self-harm in the traditional sense, where the intent is to cause physical harm.
However, the act of pulling hair can lead to physical harm over time due to hair loss and skin irritation.
Can stress reduction techniques alone stop Hair-pulling?
While stress reduction techniques can be helpful, they may not be sufficient on their own to completely stop Hair-pulling for everyone.
Combining stress reduction techniques with therapy and other coping strategies is often more effective.
Are there any medications available to treat Hair-pulling?
In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to help manage trichotillomania.
However, medication is typically used in conjunction with therapy and is not a standalone treatment.
Can children develop Hair-pulling habits?
Yes, children can develop Hair-pulling habits, and it's essential to address the behavior early to prevent it from becoming a long-term pattern.
Early intervention and support can improve the chances of successful treatment.
How long does treatment for Hair-pulling usually take?
The duration of treatment can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the Hair-pulling behavior.
Some individuals may see improvement within a few months, while others may require longer-term support.
Is Hair-pulling related to hair texture or type?
Hair-pulling can affect individuals with different hair textures and types.
It is not specific to any particular hair characteristic.
Can wearing hats or scarves prevent Hair-pulling urges?
While wearing hats or scarves may act as a barrier and temporarily prevent Hair-pulling, addressing the underlying triggers and seeking professional help is more effective in the long run.
Source:
-
Pereyra, A. D., & Saadabadi, A. (2021). Trichotillomania. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493186/
-
Mayo Clinic . (2016). Trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder) - Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/trichotillomania/symptoms-causes/syc-20355188
-
Özten, E., Hızlı Sayar, G., Kağan, G., Işık, S., Karamustafalıoğlu, O., & Eryilmaz, G. (2015). The relationship of psychological trauma with trichotillomania and skin picking. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 1203. https://doi.org/10.2147/ndt.s79554