What Is Alopecia Areata and How Can You Treat It?
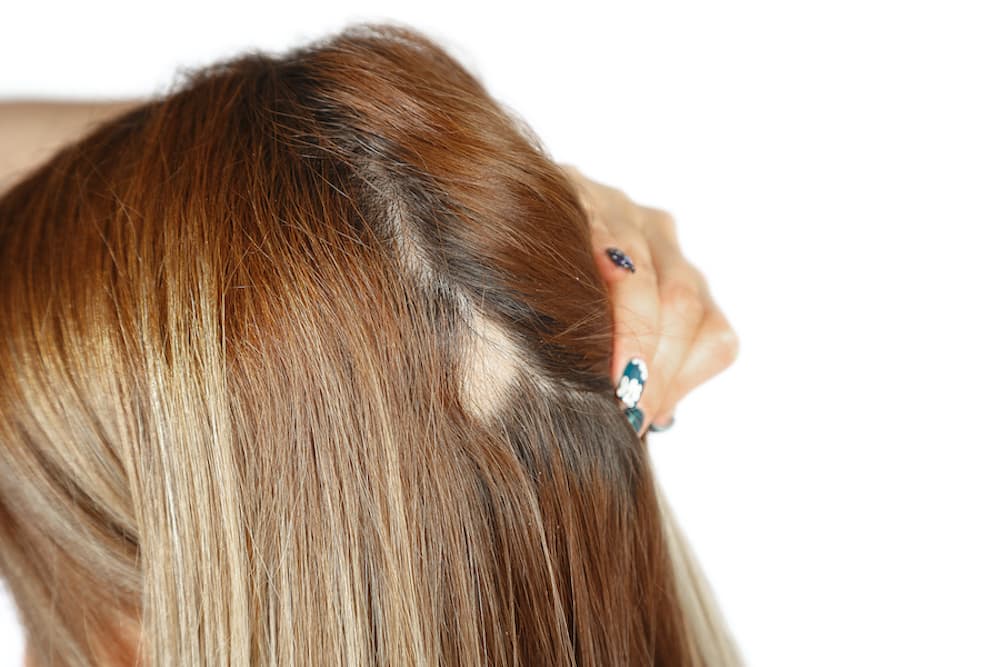
Alopecia areata is a very specific form of hair loss which may occur in 2% of people. Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss from small areas of the scalp, resulting in round shaped bald patches.
These round patches help distinguish alopecia areata from other types of hair loss, though additional testing is usually needed.
Alopecia areata can occur at any age. It rarely results in the complete loss of hair on scalp (alopecia totalis), or all over the body (alopecia universalis).
Patches can occur all over the body, but are usually found on the scalp (and beard for men).
Causes of Alopecia Areata
The exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, but most experts agree that it is an autoimmune condition. The immune cells of the body attack the hair follicles, interrupting hair growth and causing hair loss.
There may be aggravating conditions or triggers that start the cycle such as bacterial or viral infections, medications or even psychological stress. Genetic predispositions may also contribute to alopecia areata.
A dermatologist is best equipped to diagnose alopecia areata with a scalp analysis and blood tests.
How To Treat Alopecia Areata
The treatment of alopecia areata is a bit complicated. Before we dive into treatment options, here is the good news.
In many cases of alopecia areata, the condition regresses (disappears) spontaneously, leading to a full regrowth of hair in the affected areas. Unfortunately, researchers aren't sure of any specific treatments that cause the regression to occur.
Many available treatments may help regrow hair, but do not cure the problem permanently. When a person stops treatment, the newly grown hair may be lost.
Steroid Injections
Steroid injections can be quite helpful when there are only a few patches of alopecia areata. Studies confirm good results (80-90% regrowth) with this approach, but frequent injections may be required (every 4-8 weeks). If treatment is stopped, there may be a relapse.
Topical Treatments
Topical steroids can be an effective treatment for alopecia areata. A steroid cream (such as clobetasol propionate) is applied nightly to the patches of hair loss and results are evaluated in 3-4 months.
Anthralin is a topical medication created by a compounding pharmacy. It is applied topically on the scalp - it slightly irritates the skin and results in improved hair regrowth.
A topical hair growth treatment may be applied in addition to the options listed above. Minoxidil or other natural hair serums (such as the Enhance hair serum) can improve effectiveness of drugs by improving circulation and helping regrow hair.
Oral Medications
Oral immunosuppressants help tamp down the immune system so that is stops attacking hair follicles. Methotrexate is one medication that inhibits the metabolism of folic acid. While it is frequently used in the treatment of alopecia areata, it can cause serious side effect such as liver damage. In addition, methotrexate is most effective when combined with a system steroid.
Cyclosporine is another immunosuppressant which has shown mixed results in treatment of alopecia areata. Its efficacy is also improved when combined with a systemic steroid. Cyclosporine has many side effects so it should be used under strict supervision of a doctor.
There is a new class of drugs called Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors. These are the new treatments for alopecia areata. These are oral immunosuppressants used to treat alopecia areata with good results (70% regrowth). However, they are quite expensive and hair loss may relapse after patients discontinue the drug.
Systemic Steroids
High dose systemic steroids administered monthly via pulse therapy have shown to be effective at regrowing hair in alopecia areata. However, there are many side effects of this treatment including weight gain, osteoporosis, high blood pressure and menstrual irregularities.
Key Takeaways
Alopecia areata is a type of round-shaped patchy hair loss where the immune system attacks hair follicles.
In many cases alopecia areata can regress spontaneously, causing full regrowth in the affected areas.
There are many treatments for alopecia areata with mixed levels of success.
If you or a loved one is experiencing alopecia areata, it's best to see a dermatologist immediately.