
My hair has gotten much thicker, fuller and its growing long again!
– Dorit S.
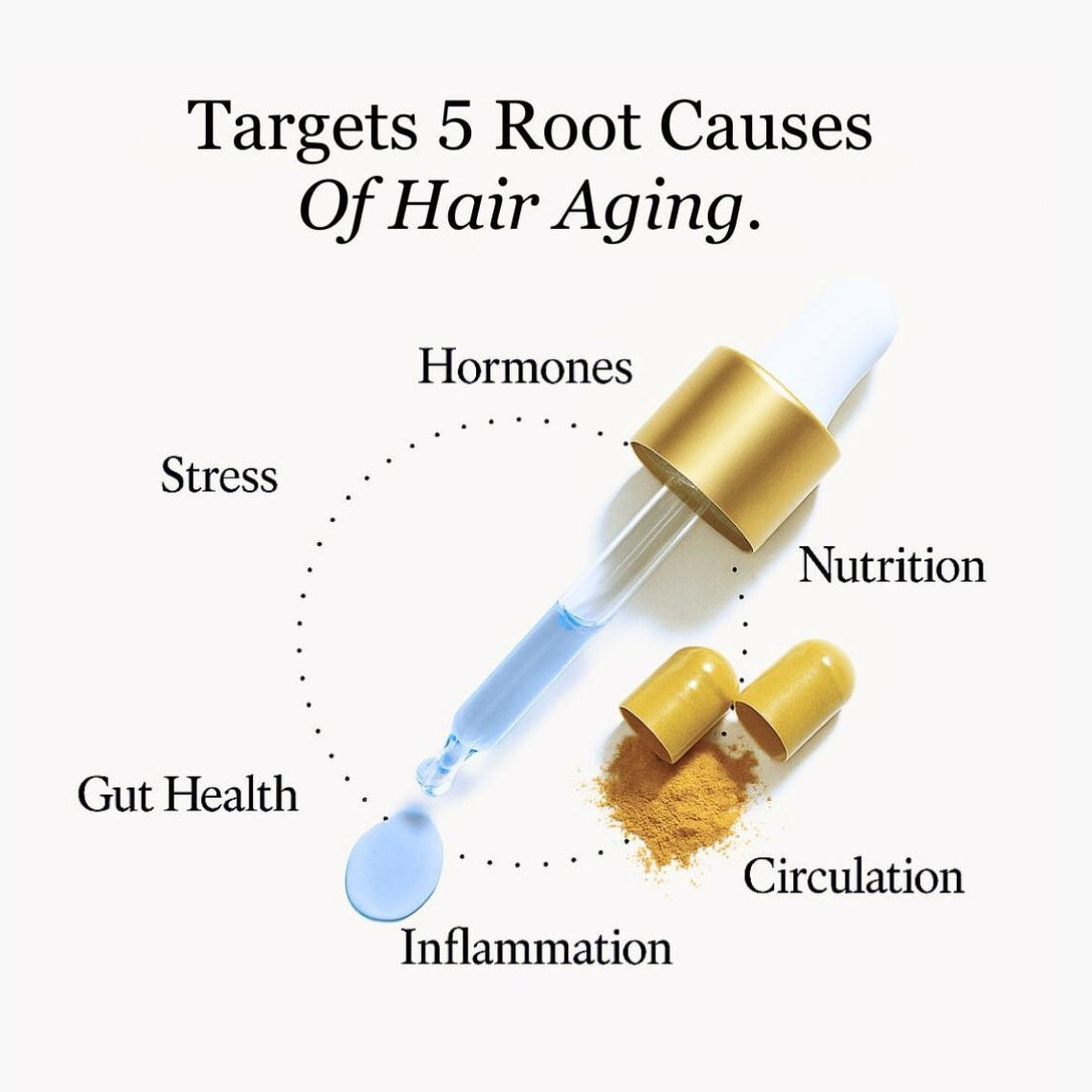
Revitalize Your Hair with Cutting-Edge Science
FullyVital is the first to bring cutting-edge, clinical anti-aging science—to restore fuller, stronger, more less gray hair at every age.
What to expect with consistent use.
Reduced hair shedding, and healthier scalp and hair.
New baby hairs. Visibly thicker and fuller hair. Less gray hairs.
Strong, voluminous and long hair. Significantly less gray hairs visible. Results keep improving.

 Rated 4.7/5 by Happy Customers
Rated 4.7/5 by Happy Customers
Clinically-backed system combats all the major root causes of hair thinning from the inside and outside with four powerful products.
 Rated 4.6/5 by Happy Customers
Rated 4.6/5 by Happy Customers
Physician formulated system combats grey hair from within and outside in with a powerful supplement and clean, oil-free serum.
This system effectively targets all the root causes of gray hairs for a youthful head of hair.


We stand behind every bottle. If you don’t see visible improvements in your hair within 120 days, simply reach out—we’ll refund your purchase. No hassle, no stress. Because results matter. And so do you.
FullyVital products target the root causes of thinning and gray hairs in the hair follicles.
That's why they work for all hair types.
Straight, wavy, curly, coily - we got you covered.
SHOP BEST SELLERS

We're here to help. Take our quiz to find solutions suitable for your hair wellness goals.

We've shared our science and research on more than 50 podcasts.

THYROID EXPERT
"I love that FullyVital is a comprehensive regrowth serum."

DETOX EXPERT
"FullyVital serum is clean and safe to use long-term."

HORMONE EXPERT
"One of the only serums that balances scalp hormones."

MENOPAUSE EXPERT
"I recommend FullyVital to all my menopausal patients."
Noticed a big reduction in hair shedding in 30 days.
Reported that hair was thicker, fuller in 60 days.
Said they saw new hair density in 90 days.
*Results from a customer survey. March 2025.